

Featured Products
Why Choose Armor Guys?
Innovative Liner & Coating Technologies
Find the Right Armor Guys Gloves for You!
Discover our diversified range of products and pick the one which suits your application best!
Liner technologies
Learn more about the technologies used in our liners.
Coatings offered
Learn more about the different coatings Armor Guys has to offer.

Standards & Norms
Learn more about the standards & norms associated with PPE.
An Array of Innovative Products
Kyorene Pro®
The 2nd generation of our patented, graphene-based gloves & sleeves, free of stainless steel and fiberglass, offering improved functionality and dexterity in general-purpose and cut-resistant styles.
SEE THE PRODUCTS >
Kyorene®
The 1st generation of our patented, graphene-based gloves & sleeves in general-purpose and cut-resistant styles.
SEE THE PRODUCTS >
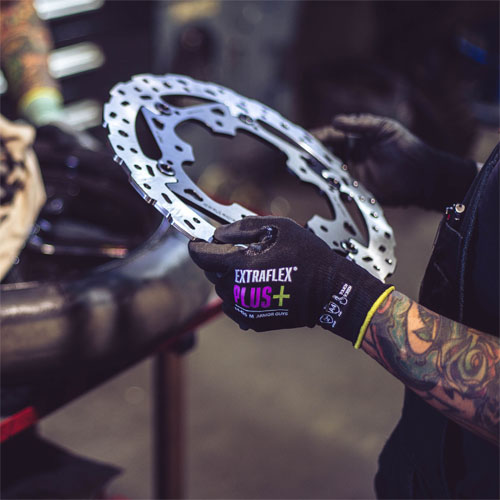
Extraflex® Plus
Improved versions of the original Extraflex® gloves that are thinner and lighter weight with increased dexterity and tactile sensitivity.
SEE THE PRODUCTS >
Extraflex®
An array of high-quality, cut-resistant and general-purpose gloves designed with engineered yarns.
SEE THE PRODUCTS >
Basetek®
Cost-effective, cut-resistant gloves & sleeves.
SEE THE PRODUCTS >
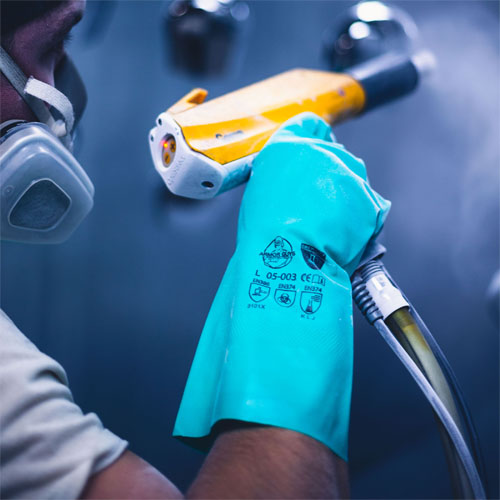
Chemiflex
Chemical-resistant options for limited applications.
SEE THE PRODUCTS >
Duty
Economical, general-purpose gloves for a variety of applications.
SEE THE PRODUCTS >
Perfotek®
High puncture-resistant gloves for specific applications.
SEE THE PRODUCTS >
Taeki5®
Cut, heat and abrasion-resistant gloves & sleeves that perform well in a variety of applications.
SEE THE PRODUCTS >
Consider Armor Guys for Your Hand Protection Needs
Feedback
ONE OF AMERICA’S LARGEST AIRLINES
Chairman of Facilities Maintenance
" Well, I can assure you, if your product is even close to the service you guys provide, you’re going to be sold out of everything, my friend. I thoroughly enjoyed you guys; you made me feel like you were there for only me, other vendors need to be taking notes from you all, especially notes on how you treated everyone.
Thank you! "
MIDLAND TOOL
Purchasing Manager
" (We) really appreciate everything about Armor Guys.
Acknowledgements are sent back quickly and everything from pricing, quantities, invoices, etc. are accurate and (Armor Guys) ships accurately and on-time with very few backorders. "
BETTS INDUSTRIES
" I haven’t had any complaints, only praise, for the Armor Guys 00-840 gloves. We have literally tried everything to destroy them. They will not cut with a razor without extreme effort; they will not degrade from metal filings and chips without extreme usage; they will not wear down chopping, splitting or stacking lumber; they do not smell after being fully submerged on a daily basis in coolants for 3 weeks. If you have anyone who questions these, please share my testimonial. "
BEARING DISTRIBUTORS
Operations Manager
(On working with Armor Guys)
“Thank you for this. I am very impressed so far with the response and the service.”
BETTS INDUSTRIES
“ The fully covered nitrile gloves (00-845) will not leak being after being fully submerged for 15 minutes, nor after 2 weeks of repeated usage on our saws, in direct contact with coolants, lubricants or the stopped blades themselves. Metal stampers are able to get 2 full weeks of usage and only requested a new pair due to the dirty nature of his gloves; otherwise, they were still 100% functional after the 2 weeks. ”













